Introduction to Revit
Autodesk Revit isn’t just software; it’s the beating heart of modern Building Information Modeling (BIM) for architects, engineers, and contractors globally. As the flagship BIM platform from industry giant Autodesk, Revit transcends simple 3D modeling. It creates intelligent, data-rich building models that streamline every project phase – from initial concept sketches to facility management. This 2025 guide for 3D Modeling in Revit cuts through the noise, delivering everything a newcomer needs to understand Revit’s power, applications, and learning path.
Understanding Revit’s Core & Evolution
What Exactly Is Revit?
- BIM Engine: Revit is fundamentally a BIM platform. It creates intelligent 3D models where elements (walls, beams, ducts) carry crucial data (material, cost, performance specs), not just geometry.
- Parametric Powerhouse: Change a dimension in one view (e.g., a plan), and Revit automatically updates every related view (sections, elevations, schedules) – ensuring absolute consistency and saving immense time.
- Centralized Model Database: All project information resides in a single, coordinated model, enabling seamless collaboration and reducing errors.
A Brief History: From Startup to Industry Standard
- Origins: Born in 2000 as the brainchild of Revit Technology Corporation, its core innovation was parametric building modeling.
- Autodesk Era: Acquired in 2002, Autodesk propelled Revit into the mainstream, integrating deep BIM functionality and expanding its capabilities across disciplines (Architecture, Structure, MEP).
- The BIM Revolution: Revit became the catalyst, moving the AEC industry from isolated 2D CAD workflows to integrated, data-driven 3D BIM processes.
Crucial Clarification: Revit vs. BIM vs. CAD
- Revit is NOT BIM: BIM is the overarching methodology – the process of creating and managing intelligent building information. Revit is a primary software tool enabling that methodology.
- Revit vs. CAD: Traditional CAD (e.g., AutoCAD) focuses on creating 2D lines or standalone 3D shapes. Revit creates intelligent, data-rich building objects within a coordinated model. CAD = digital drafting board. Revit = virtual building simulation.
Unleashing Revit’s Power: Key Features & Capabilities
Revit’s strength lies in its integrated ecosystem:
Parametric & Intelligent Modeling:
- Create walls that know their materials and fire ratings, doors that schedule automatically, beams that carry structural loads. Change a parameter, and the model updates intelligently.
Automated Documentation:
- Plans, sections, elevations, schedules, and details are dynamically generated directly from the 3D model. No more manual coordination! Change the model, and drawings update instantly.
Multi-Disciplinary Design & Collaboration (The BIM Advantage):
- Architecture, Structure, MEP: Dedicated toolsets within one platform allow architects, structural engineers, and MEP engineers to work collaboratively on the same coordinated model.
- Cloud Collaboration: Autodesk Construction Cloud (ACC/BIM 360) enables real-time co-authoring, clash detection, and centralized model management for distributed teams.
Analysis & Simulation (Beyond Geometry):
- Integrate energy analysis, daylighting studies, structural load calculations, and clash detection (often via Navisworks) directly using the rich model data for smarter, more sustainable design decisions.
Visualization & Client Communication:
- Generate compelling presentations, renderings (via built-in tools or plugins like Enscape/Twinmotion), and even VR walkthroughs directly from the BIM model.
Revit Across the AEC Spectrum
Revit adapts to diverse roles:
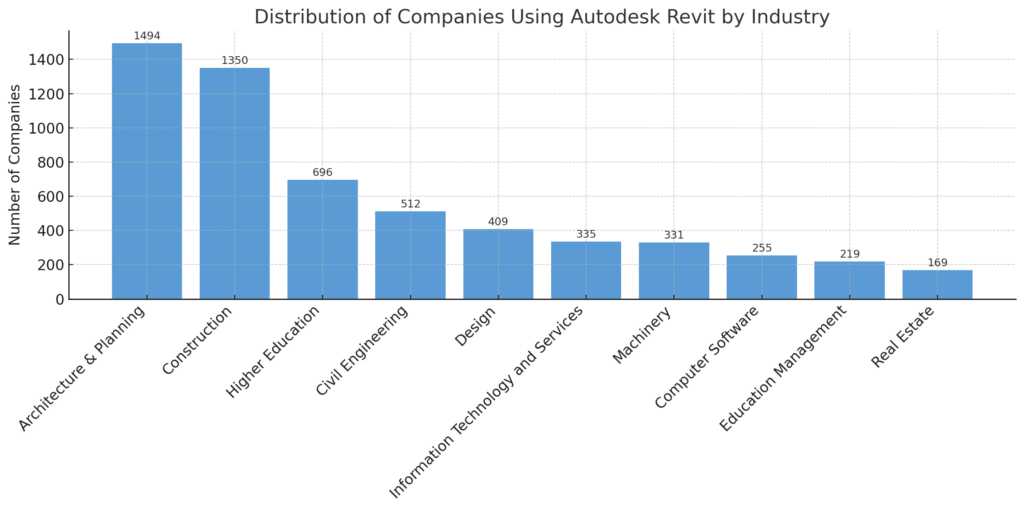
- Architects & Designers: Conceptual massing, detailed building modeling, space planning, automated documentation, rendering, facade studies, energy analysis.
- Structural Engineers: Modeling structural frames (steel, concrete, timber), rebar detailing, generating fabrication drawings, integrating analysis software.
- MEP Engineers (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing): Designing complex ductwork, piping, electrical systems within the building context, performing calculations, ensuring spatial coordination.
- Contractors & Construction Managers: Utilizing models for 4D (scheduling) and 5D (cost) BIM, clash detection, construction sequencing, prefabrication planning, and field coordination.
The Learning Curve: Mastering Revit
Is Revit Hard to Learn?
- Honest Answer: It has a steeper initial learning curve than simpler modelers like SketchUp. Its power comes with complexity – ribbons, numerous settings, and the fundamental shift from CAD drafting to BIM thinking.
- The Payoff: Immense. Proficiency in Revit significantly boosts efficiency, accuracy, collaboration, and employability. The ROI on time invested is very high.
Effective Learning Strategies:
- Structured Courses: Highly recommended. Look for courses covering core modeling (walls, floors, roofs, stairs), family creation, documentation (views, sheets, annotations), and collaboration. (Novatr’s BIM Course is one structured option).
- Project-Based Practice: Learning is solidified by applying skills to real-world project scenarios.
- Focus Fundamentals First: Master basic modeling and documentation before diving into advanced plugins or complex geometry.
- Leverage Resources: Autodesk University, official forums, YouTube channels (e.g., Balkan Architect, The Revit Kid), and dedicated blogs are invaluable.
Revit in the 2025 Ecosystem: Plugins, Rendering & Alternatives
Essential Plugins (Supercharging Revit):
- Dynamo: Visual scripting for automation (repetitive tasks), complex parametric design, and data management. Crucial for efficiency.
- Rhino.Inside.Revit: Seamlessly integrates Rhino/Grasshopper’s advanced freeform modeling and parametric control directly into the Revit environment. Key for complex geometry.
- Enscape / Twinmotion: Real-time rendering and immersive visualization plugins for stunning client presentations directly from the Revit viewport.
- pyRevit: A powerhouse collection of productivity tools, UI enhancements, and utilities created by the community.
- IdeateApps / BIMTrack / DiRoots: Popular suites for model management, auditing, clash resolution, and productivity boosts.
Rendering Options:
- Cloud Rendering (Autodesk): Leverage cloud power for high-quality, complex, or batch renders without tying up your workstation.
- Real-Time Plugins (Enscape, Twinmotion): Offer incredible speed and interactivity for design exploration and client reviews.
- Dedicated Renderers (V-Ray, Corona): Provide the highest level of photorealism for final presentations (often requiring export).
Revit Alternatives:
- ArchiCAD (GRAPHISOFT): A mature, architect-focused BIM platform, often praised for its intuitive interface and strong native capabilities. Popular in specific regions (Europe, Australia). Excellent IFC support.
- Vectorworks Architect: Known for its flexibility, strong 2D/3D hybrid workflow, and suitability for smaller firms or design-focused practices. Includes robust BIM tools.
- Bentley OpenBuildings Designer: A powerhouse for large-scale, complex infrastructure projects (airports, hospitals). Steeper learning curve, significant cost.
Key Takeaway: Revit dominates in large-firm collaboration and MEP/Structural integration. ArchiCAD excels in architectural design workflow. Vectorworks offers flexibility for smaller studios. The “best” depends on project type, team size, and regional preferences.
Getting Started with 3D Modeling in Revit
Licensing & Cost:
- Subscription Model: Revit is only available via subscription. Current 2025 options:
- Monthly: ~$365
- Annual: ~$2,910
- 3-Year: ~$8,730
- Free Access: Students and Educators can obtain free educational licenses valid for 1 year (renewable) directly from Autodesk.
System Requirements:
- Demanding: Revit requires a powerful workstation. Prioritize:
- CPU: High clock speed (Intel i7/i9 or AMD Ryzen 7/9 equivalent).
- RAM: Minimum 16GB, 32GB+ highly recommended for complex projects.
- GPU: Dedicated mid-to-high-range workstation card (NVIDIA RTX A-series or Quadro RTX, AMD Radeon Pro W-series). Gaming cards work but lack certified drivers.
- Storage: Fast SSD (NVMe preferred) – 500GB+ minimum.
- Check Autodesk: Always verify the latest official system requirements before purchasing hardware.
Conclusion: Your 3D Modeling in Revit Journey Begins
Autodesk Revit remains the undisputed cornerstone of professional BIM workflows in 2025. Its ability to integrate intelligent modeling, automated documentation, multi-disciplinary coordination, and data-driven analysis makes it indispensable for creating efficient, sustainable, and constructible buildings. While mastering its depth takes dedication, the career opportunities and professional capabilities it unlocks are substantial.

